How To Enable Firewall In Windows 7 Using Command Prompt
Configure Windows Firewall using command line
Allow's see manual configuring Windows Firewall using GUI and using command line. Possibilities of configuring Windows Firewall from command line are identical possibilities of configuring from GUI. Using command line allows you create batch file to run on other computers so you lot tin essentially shorten a time spending for configuring firewall on workstations according to your requirements.
This commodity examines how to configure Windows Firewall using the Netsh control-line utility.
Windows XP Service Pack 2 (SP2) includes the Windows Firewall, a replacement for the feature previously known every bit the Internet Connection Firewall (ICF). Windows Firewall is a stateful host firewall that drops all unsolicited incoming traffic that does not correspond to either traffic sent in response to a request of the computer (solicited traffic) or unsolicited traffic that has been specified as allowed (excepted traffic). This behavior of Windows Firewall provides a level of protection from malicious users and programs that use unsolicited incoming traffic to attack computers. With the exception of some Net Control Message Protocol (ICMP) letters, Windows Firewall does not drop outgoing traffic. Windows Firewall is also included with Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 (SP1).
Now we configure Windows Firewall step-past-step
Stride ane. Windows Firewall: General
The Full general tab with its default settings is shown in the post-obit effigy.
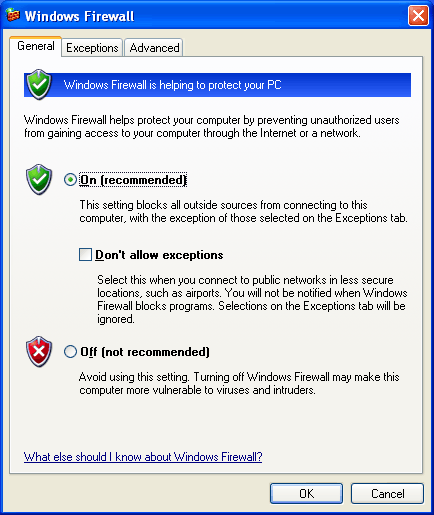
From the General tab, you can select the post-obit:
- On (recommended) - Select to enable Windows Firewall for all of the network connections that are selected on the Advanced tab. Windows Firewall is enabled to allow only solicited and excepted incoming traffic. Excepted traffic is configured on the Exceptions tab.
- Don't allow exceptions - Click to permit merely solicited incoming traffic. Excepted incoming traffic is non allowed. The settings on the Exceptions tab are ignored and all of the network connections are protected, regardless of the settings on the Avant-garde tab.
- Off (not recommended) - Select to disable Windows Firewall. This is not recommended, especially for network connections that are direct accessible from the Internet, unless yous are already using a 3rd-party host firewall product.
Enable/Disable Windows firewall using control line
netsh firewall set opmode [ manner = ] ENABLE|DISABLE [ [ exceptions = ] ENABLE|DISABLE [ profile = ] CURRENT|DOMAIN|STANDARD|ALL [ interface = ] name ]
Sets firewall operational configuration.
Parameters:
mode - Operational mode.
ENABLE - Enable firewall. DISABLE - Disable firewall.
exceptions - Exception way (optional).
ENABLE - Permit through firewall (default). DISABLE - Do not allow through firewall.
profile - Configuration profile (optional).
Current - Electric current profile (default). DOMAIN - Domain profile. STANDARD - Standard profile. ALL - All profiles.
interface - Interface name (optional).
Examples:
Enable the Firewall:
netsh firewall set opmode enable
Enable the Firewall and DO NOT Permit Port/Program Exceptions:
netsh firewall ready opmode enable disable
Enable Firewall and Permit Port/Program Exceptions:
netsh firewall ready opmode enable enable
Disable the Firewall:
netsh firewall set opmode disable
Step 2. Windows Firewall: Exceptions
The following effigy shows the Exceptions tab with its settings.
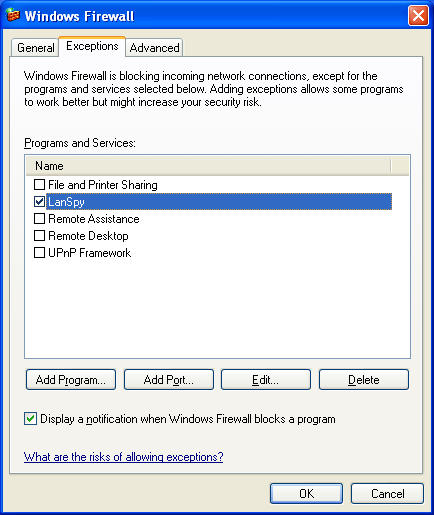
From the Exceptions tab, y'all tin enable or disable an existing program (an application or service) or port or maintain the list of programs and ports that define excepted traffic. The excepted traffic is non allowed when the Don't allow exceptions pick is selected on the General tab.
Add together plan-based exception to Exceptions listing in Windows Firewall
To add a program exception, click Add together Program. The Add Program dialog box is displayed from which you can select a program or browse for a program'due south file proper noun. The post-obit figure shows an example.
Add/Alter program-based exception using command line
netsh firewall add allowedprogram
Used to add a plan-based exception.
netsh firewall set allowedprogram
Used to change the settings of an existing program-based exception.
Syntax and parameters of commands add together and set are identical.
Syntax:
Note: Some parts of the following code snippet have been displayed in multiple lines only for better readability. These should be entered in a single line.
netsh firewall add allowedprogram [ program = ] path [ name = ] name [ [ mode = ] ENABLE|DISABLE [ telescopic = ] ALL|SUBNET|CUSTOM [ addresses = ] addresses [ contour = ] Electric current|DOMAIN|STANDARD|ALL ]
Adds firewall allowed program configuration.
Parameters:
programme - Program path and file name.
name - Program proper noun.
way - Program mode (optional).
ENABLE - Allow through firewall (default). DISABLE - Exercise non allow through firewall.
scope - Program scope (optional).
ALL - Allow all traffic through firewall (default). SUBNET - Permit only local network (subnet) traffic through firewall. CUSTOM - Allow only specified traffic through firewall.
addresses - Custom telescopic addresses (optional).
contour - Configuration profile (optional).
CURRENT - Current profile (default). DOMAIN - Domain profile. STANDARD - Standard profile. ALL - All profiles.
Remarks: 'telescopic' must be 'CUSTOM' to specify 'addresses'.
Examples:
netsh firewall add together allowedprogram C:\MyApp\MyApp.exe MyApp ENABLE netsh firewall add allowedprogram C:\MyApp\MyApp.exe MyApp DISABLE netsh firewall add together allowedprogram C:\MyApp\MyApp.exe MyApp ENABLE CUSTOM 157.threescore.0.i,172.sixteen.0.0/16,x.0.0.0/255.0.0.0,LocalSubnet netsh firewall add allowedprogram program = C:\MyApp\MyApp.exe proper noun = MyApp mode =ENABLE netsh firewall add allowedprogram program = C:\MyApp\MyApp.exe proper name = MyApp mode = DISABLE netsh firewall add together allowedprogram programme = C:\MyApp\MyApp.exe name = MyApp mode = ENABLE scope = CUSTOM 157.sixty.0.1,172.16.0.0/16,10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0,LocalSubnet
Delete existing program-based exception using command line
netsh firewall delete allowedprogram
Used to delete an existing program-based exception.
Syntax:
Annotation: Some parts of the following code snippet have been displayed in multiple lines simply for better readability. These should be entered in a single line.
netsh firewall delete allowedprogram [ plan = ] path [ [ profile = ] Current|DOMAIN|STANDARD|ALL ]
Deletes firewall immune program configuration.
Parameters:
program - Program path and file name.
contour - Configuration profile (optional).
Electric current - Current profile (default). DOMAIN - Domain profile. STANDARD - Standard profile. ALL - All profiles.
Examples:
delete allowedprogram C:\MyApp\MyApp.exe delete allowedprogram program = C:\MyApp\MyApp.exe
Add a Port to Exceptions list
To add together a port exception, click AddPort. The Add a Port dialog box is displayed, from which you can configure a TCP or UDP port. The post-obit figure shows an example.
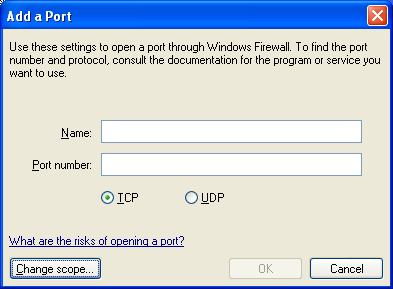
Windows Firewall allows you lot to specify the scope of excepted traffic. The scope defines the portion of the network from which the excepted traffic is allowed to originate. To define the telescopic for a plan or port, click Change Scope. The following figure shows an case.
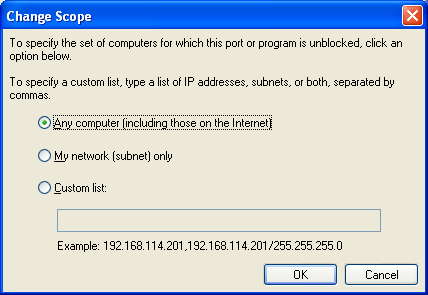
Add together/Modify port-based exception using command line
netsh firewall add together portopening
Used to create a port-based exception.
netsh firewall set portopening
Used to modify the settings of an existing port-based exception.
Syntax and parameters of commands add together and set are identical.
Syntax:
Note: Some parts of the following lawmaking snippet have been displayed in multiple lines but for better readability. These should be entered in a unmarried line.
netsh firewall add portopening [ protocol = ] TCP|UDP|ALL [ port = ] one-65535 [ name = ] name [ [ mode = ] ENABLE|DISABLE [ scope = ] ALL|SUBNET|CUSTOM [ addresses = ] addresses [ profile = ] CURRENT|DOMAIN|STANDARD|ALL [ interface = ] proper noun ]
Adds firewall port configuration.
Parameters:
protocol - Port protocol.
TCP - Transmission Command Protocol (TCP). UDP - User Datagram Protocol (UDP). ALL - All protocols.
port - Port number.
proper noun - Port name.
mode - Port mode (optional).
ENABLE - Allow through firewall (default). DISABLE - Do non allow through firewall.
scope - Port scope (optional).
ALL - Permit all traffic through firewall default). SUBNET - Allow only local network (subnet) traffic through firewall. CUSTOM - Allow merely specified traffic through firewall.
addresses - Custom scope addresses (optional).
profile - Configuration profile (optional).
CURRENT - Electric current contour (default). DOMAIN - Domain profile. STANDARD - Standard profile. ALL - All profiles.
interface - Interface name (optional).
Remarks:
'profile' and 'interface' may non be specified together. 'scope' and 'interface' may non be specified together. 'scope' must be 'CUSTOM' to specify 'addresses'.
Examples:
netsh firewall add portopening TCP 80 MyWebPort netsh firewall add portopening UDP 500 IKE ENABLE ALL netsh firewall add portopening ALL 53 DNS ENABLE CUSTOM 157.60.0.ane,172.xvi.0.0/sixteen,10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0,LocalSubnet netsh firewall add portopening protocol = TCP port = eighty proper name =MyWebPort netsh firewall add portopening protocol = UDP port = 500 proper noun = IKE mode = ENABLE scope = ALL netsh firewall add together portopening protocol = ALL port = 53 name =DNS mode = ENABLE scope = CUSTOM addresses = 157.sixty.0.1,172.16.0.0/sixteen,ten.0.0.0/255.0.0.0,LocalSubnet
Delete existing port-based exception using command line
netsh firewall delete portopening
Used to delete an existing port-based exception.
Syntax:
Annotation: Some parts of the following code snippet have been displayed in multiple lines simply for better readability. These should be entered in a single line.
netsh firewall delete portopening [ protocol = ] TCP|UDP|ALL [ port = ] i-65535 [ [ profile = ] CURRENT|DOMAIN|STANDARD|ALL [ interface = ] name ]
Deletes firewall port configuration.
Parameters:
protocol - Port protocol.
TCP - Manual Control Protocol (TCP). UDP - User Datagram Protocol (UDP). ALL - All protocols.
port - Port number.
profile - Configuration profile (optional).
Electric current - Current contour (default). DOMAIN - Domain profile. STANDARD - Standard profile. ALL - All profiles.
interface - Interface name (optional).
Remarks:
'contour' and 'interface' may not be specified together. Examples:
netsh firewall delete portopening TCP eighty netsh firewall delete portopening UDP 500 netsh firewall delete portopening protocol = TCP port = 80 netsh firewall delete portopening protocol = UDP port = 500
Windows Firewall Notifications
Applications can employ Windows Firewall application programming interface (API) function calls to automatically add exceptions. When applications create exceptions using the Windows Firewall APIs, the user is not notified. If the application using the Windows Firewall APIs does not specify an exception proper name, the exception is non displayed in the exceptions list on the Exceptions tab of the Windows Firewall.

When an awarding that does non apply the Windows Firewall API runs and attempts to listen on TCP or UDP ports, Windows Firewall prompts a local administrator with a Windows Security Alarm dialog box. The following effigy shows an instance.
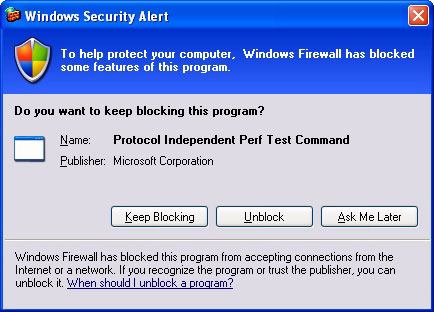
Set option "Display a notification when Windows Firewall blocks a program" using command line
netsh firewall set notifications
Used to specify the notification beliefs.
Syntax:
Notation: Some parts of the post-obit lawmaking snippet accept been displayed in multiple lines just for better readability. These should exist entered in a single line.
netsh firewall ready notifications [ mode = ] ENABLE|DISABLE [ [ profile = ] Current|DOMAIN|STANDARD|ALL ]
Sets firewall notification configuration.
Parameters:
mode - Notification mode.
ENABLE - Allow pop-up notifications from firewall. DISABLE - Do non let popular-upward notifications from firewall.
contour - Configuration profile (optional).
CURRENT - Current contour (default). DOMAIN - Domain profile. STANDARD - Standard contour. ALL - All profiles.
Examples:
netsh firewall set notifications ENABLE netsh firewall prepare notifications DISABLE netsh firewall set notifications manner = ENABLE netsh firewall netsh firewall fix notifications mode = DISABLE
Stride 3. Windows Firewall: Avant-garde Options
The following figure shows the Avant-garde tab.
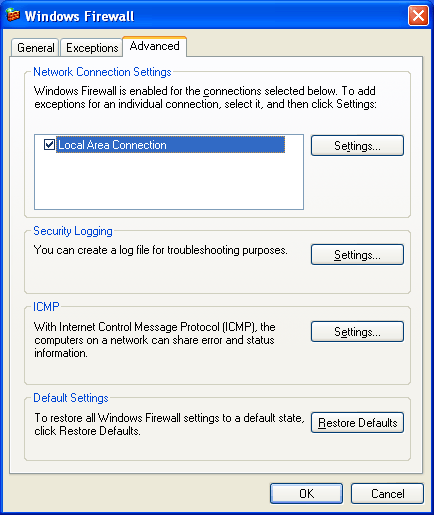
The Advanced tab contains the following sections:
-
Network Connexion Settings
-
Security Logging
-
ICMP
-
Default Settings
Network Connections Settings
In Network Connection Settings, you can:
-
Specify the set of interfaces on which Windows Firewall is enabled. To enable, select the check box next to the network connection name. To disable, clear the check box. By default, all of the network connections have Windows Firewall enabled. If a network connectedness does not appear in this listing, then information technology is not a standard networking connexion. Examples include some custom dialers from Internet service providers (ISPs).
-
Configure avant-garde settings of an individual network connection past clicking the network connection name, and then clicking Settings.
If yous clear all of the check boxes in the Network Connection Settings, then Windows Firewall is not protecting your computer, regardless of whether yous have selected On (recommended) on the Full general tab. The settings in Network Connection Settings are ignored if you have selected Don’t allow exceptions on the General tab, in which case all interfaces are protected.
When you click Settings, the Advanced Settings dialog box is displayed, as shown in the following figure.
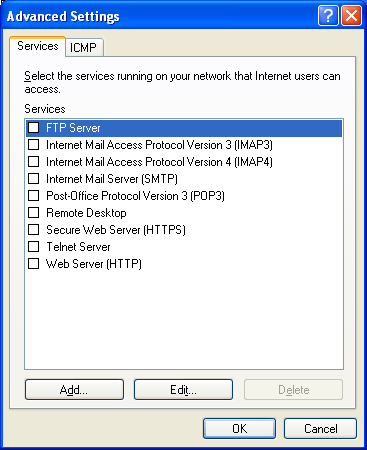
From the Advanced Settings dialog box, you can configure specific services from the Services tab (by TCP or UDP port only) or enable specific types of ICMP traffic from the ICMP tab.
On the Services tab, do one of the post-obit:
-
If you want to enable a service, under Services select the check box next to service that you want to enable, and then enter the required data.
-
If you lot desire to add together a service definition, click Add, and then enter the required data.
-
If you lot want to edit a service definition, click the service that you want to edit, click Edit, and and so modify the advisable information.
-
If you desire to delete a service definition, click the service that you want to delete, and and so click Delete.
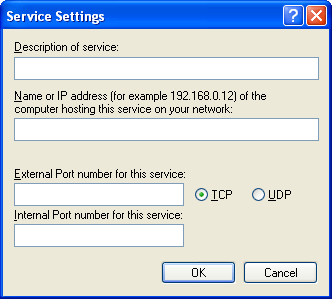
Notes:
-
No two service definitions tin can use the same port numbers simultaneously.
-
For service definitions that are preconfigured, you tin edit merely the field that is labeled Name or IP address of the computer hosting this service on your network.
-
For service definitions that you have added, yous tin can edit just the fields that are labeled Proper noun or IP address of the computer hosting this service on your network, External Port number for this service, and Internal Port number for this service.
-
You can delete simply the service definitions that you have added. You cannot delete service definitions that are preconfigured.
On the ICMP tab, do i of the following:
-
To enable Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) options, select the check box adjacent to each type of asking for data to which you would like your computer to respond.
-
To disable ICMP options, clear whatsoever or all of the ICMP check boxes.
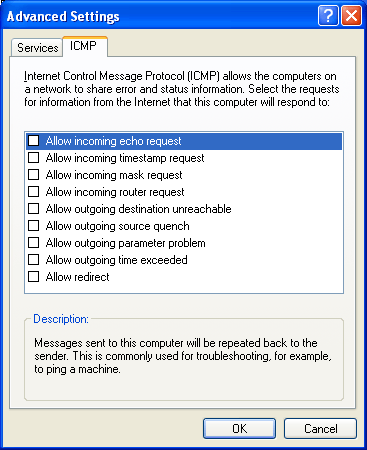
Enable or disable Windows Firewall pre-defined services using control line
netsh firewall set service
Used to enable or disable the pre-divers file and printer sharing, remote assistants, remote desktop, and UPnP exceptions.
Syntax:
Note: Some parts of the following lawmaking snippet take been displayed in multiple lines but for meliorate readability. These should be entered in a single line.
netsh firewall set service [ type = ] FILEANDPRINT|REMOTEADMIN|REMOTEDESKTOP|UPNP|ALL [ [ mode = ] ENABLE|DISABLE [ scope = ] ALL|SUBNET|CUSTOM [ addresses = ] addresses [ contour = ] Electric current|DOMAIN|STANDARD|ALL ]
Sets firewall service configuration.
Parameters:
type - Service blazon.
FILEANDPRINT - File and printer sharing. REMOTEADMIN - Remote administration. REMOTEDESKTOP - Remote assistance and remote desktop. UPNP - UPnP framework. ALL - All types.
manner - Service mode (optional).
ENABLE - Allow through firewall (default). DISABLE - Do not allow through firewall.
scope - Service scope (optional).
ALL - Permit all traffic through firewall(default). SUBNET - Allow only local network (subnet) traffic through firewall. CUSTOM - Allow only specified traffic through firewall.
addresses - Custom scope addresses (optional).
contour - Configuration contour (optional).
Electric current - Current profile (default). DOMAIN - Domain profile. STANDARD - Standard profile. ALL - All profiles.
Remarks:
-
'scope' ignored if 'mode' is DISABLE.
-
'scope' must exist 'CUSTOM' to specify'addresses'.
Examples:
netsh firewall set service FILEANDPRINT netsh firewall fix service REMOTEADMIN ENABLE SUBNET netsh firewall set service REMOTEDESKTOP ENABLE CUSTOM 157.60.0.one,172.16.0.0/16,10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0,LocalSubnet netsh firewall set service type = FILEANDPRINT netsh firewall prepare service type = REMOTEADMIN mode = ENABLE scope = SUBNET netsh firewall set service blazon = REMOTEDESKTOP manner = ENABLE scope = CUSTOM addresses = 157.60.0.1,172.16.0.0/xvi,10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0,LocalSubnet
Set up Windows Firewall Security Logging

In Security Logging, click Settings to specify the configuration of Windows Firewall logging in the Log Settings dialog box, as shown in the following figure
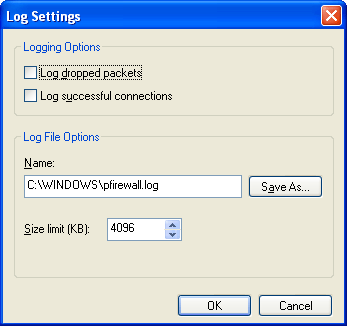
From the Log Settings dialog box, you lot can configure whether to log discarded (dropped) packets or successful connections and specify the proper name and location of the log file (past default fix to Systemroot\pfirewall.log) and its maximum size.
Set Windows Firewall Security Logging using command line
netsh firewall set up logging
Used to specify logging options.
Syntax:
Notation Some parts of the following lawmaking snippet accept been displayed in multiple lines only for better readability. These should be entered in a single line.
netsh firewall gear up logging [ [ filelocation = ] path [ maxfilesize = ] 1-32767 [ droppedpackets = ] ENABLE|DISABLE [ connections = ] ENABLE|DISABLE ]
Sets firewall logging configuration.
Parameters:
filelocation - Log path and file name (optional).
maxfilesize - Maximum log file size in kilobytes (optional).
droppedpackets - Dropped packet log mode (optional).
ENABLE - Log in firewall. DISABLE - Practise not log in firewall.
connections - Successful connection log mode (optional).
ENABLE - Log in firewall. DISABLE - Do non log in firewall.
Remarks:
At least one parameter must be specified. Examples:
netsh firewall ready logging %windir%\pfirewall.log 4096 netsh firewall set logging %windir%\pfirewall.log 4096 ENABLE netsh firewall fix logging filelocation = %windir%\pfirewall.log maxfilesize = 4096 netsh firewall set logging filelocation = %windir%\pfirewall.log maxfilesize = 4096 droppedpackets = ENABLE
ICMP Settings
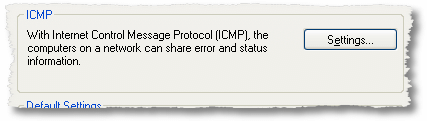
In ICMP, click Settings to specify the types of ICMP traffic that are immune in the ICMP dialog box, every bit shown in the following figure.
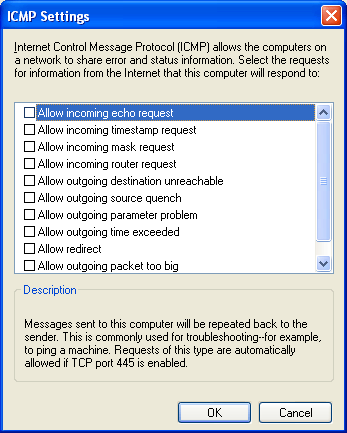
From the ICMP dialog box, you tin enable and disable the types of incoming ICMP messages that Windows Firewall allows for all the connections selected on the Advanced tab. ICMP messages are used for diagnostics, reporting mistake conditions, and configuration. By default, no ICMP messages in the list are allowed.
A common stride in troubleshooting connectivity problems is to apply the Ping tool to ping the address of the computer to which you are trying to connect. When you ping, yous send an ICMP Echo message and get an ICMP Repeat Reply message in response. By default, Windows Firewall does not allow incoming ICMP Echo letters and therefore the figurer cannot ship an ICMP Echo Reply in response. To configure Windows Firewall to permit the incoming ICMP Echo message, yous must enable the Allow incoming echo request setting. Prepare Windows Firewall ICMP Settings using command line
netsh firewall set icmpsetting
Used to specify excepted ICMP traffic.
Syntax:
Note Some parts of the following code snippet have been displayed in multiple lines only for better readability. These should be entered in a single line.
netsh firewall set icmpsetting [ type = ] 2-5|8-9|eleven-13|17|ALL [ [ fashion = ] ENABLE|DISABLE [ profile = ] CURRENT|DOMAIN|STANDARD|ALL [ interface = ] name ]
Sets firewall ICMP configuration.
Parameters:
blazon - ICMP type.
2 - Permit outgoing packet too large. 3 - Permit outgoing destination unreachable. 4 - Allow outgoing source quench. 5 - Allow redirect. viii - Let incomming echo asking. nine - Allow incomming router request. 11 - Allow approachable time exceeded. 12 - Allow outgoing parameter problem. thirteen - Let incomming timestamp request. 17 - Permit incomming mask request. ALL - All types.
mode - ICMP mode (optional).
ENABLE - Allow through firewall (default). DISABLE - Do not permit through firewall.
profile - Configuration profile (optional).
CURRENT - Current contour (default). DOMAIN - Domain contour. STANDARD - Standard contour. ALL - All profiles.
interface - Interface name (optional).
Remarks:
'profile' and 'interface' may not be specified together. 'type' 2 and 'interface' may not be specified together.
Examples:
netsh firewall ready icmpsetting 8 netsh firewall ready icmpsetting 8 ENABLE netsh firewall set icmpsetting ALL DISABLE netsh firewall set icmpsetting blazon = viii netsh firewall prepare icmpsetting type = eight mode = ENABLE netsh firewall set icmpsetting type = ALL mode = DISABLE
Configure unicast response to a multicast or broadcast asking behavior using command line
netsh firewall set multicastbroadcastresponse
Used to specify the unicast response to a multicast or broadcast request beliefs.
Syntax:
Note:Some parts of the post-obit code snippet accept been displayed in multiple lines only for better readability. These should be entered in a unmarried line.
netsh firewall set multicastbroadcastresponse [ way = ] ENABLE|DISABLE [ [ profile = ] Current|DOMAIN|STANDARD|ALL ]
Sets firewall multicast/broadcast response configuration.
Parameters:
mode - Multicast/broadcast response style.
ENABLE - Allow responses to multicast/broadcast traffic through the firewall. DISABLE - Do non allow responses to multicast/circulate traffic through the firewall.
profile - Configuration profile (optional).
Current - Electric current contour (default). DOMAIN - Domain contour. STANDARD - Standard profile. ALL - All profiles.
Examples:
netsh firewall set multicastbroadcastresponse ENABLE netsh firewall prepare multicastbroadcastresponse DISABLE netsh firewall set multicastbroadcastresponse manner = ENABLE netsh firewall fix multicastbroadcastresponse style = DISABLE
Restore all Windows Firewall settings to default state
In Advanced Tab Click Restore Defaults to reset Windows Firewall back to its originally installed state. When you click Restore Defaults, you are prompted to verify your decision earlier Windows Firewall settings are changed.
Restore all Windows Firewall settings to default land using command line
netsh firewall reset
Used to reset the configuration of Windows Firewall to default settings. There are no command line options for the reset command.
Brandish Windows Firewall settings using command line
netsh firewall show commands
The following show commands are used to brandish the current configuration:
-
show allowedprogram - Displays the excepted programs.
-
show config - Displays the local configuration information.
-
show currentprofile - Displays the current profile.
-
show icmpsetting - Displays the ICMP settings.
-
testify logging - Displays the logging settings.
-
evidence multicastbroadcastresponse - Displays multicast/broadcast response settings.
-
show notifications - Displays the current settings for notifications.
-
show opmode - Displays the operational mode.
-
show portopening - Displays the excepted ports.
-
prove service - Displays the services.
-
show state - Displays the current state information.
For boosted information about the show config and bear witness state commands, see Troubleshooting Windows Firewall in Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack two.
Similar articles
- Managing DHCP from PowerShell
- Viewing Network Settings from PowerShell
- Pinging from PowerShell
- Creating and Manipulating Network Shares with Powershell
Source: https://lizardsystems.com/articles/configure-windows-firewall-using-command-line/
Posted by: fuentespasomenton.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Enable Firewall In Windows 7 Using Command Prompt"
Post a Comment